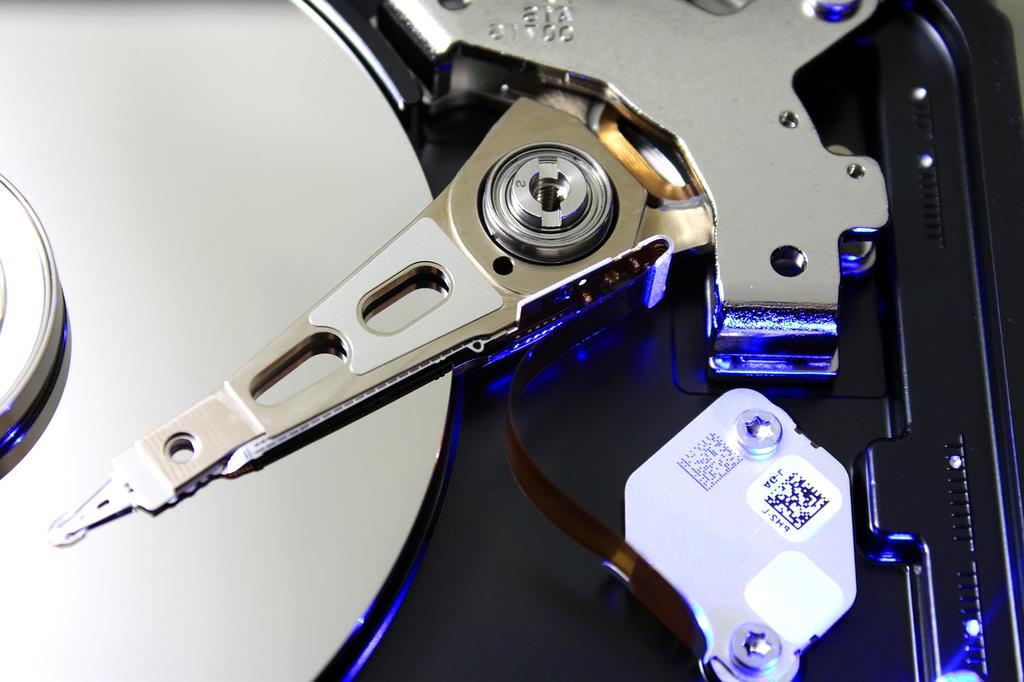
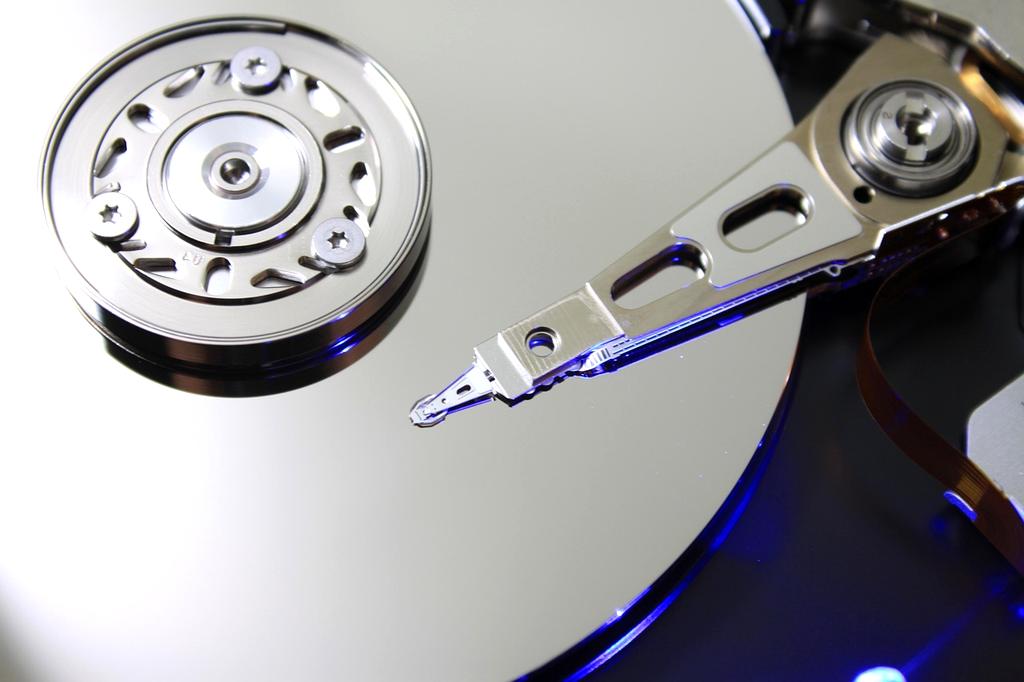
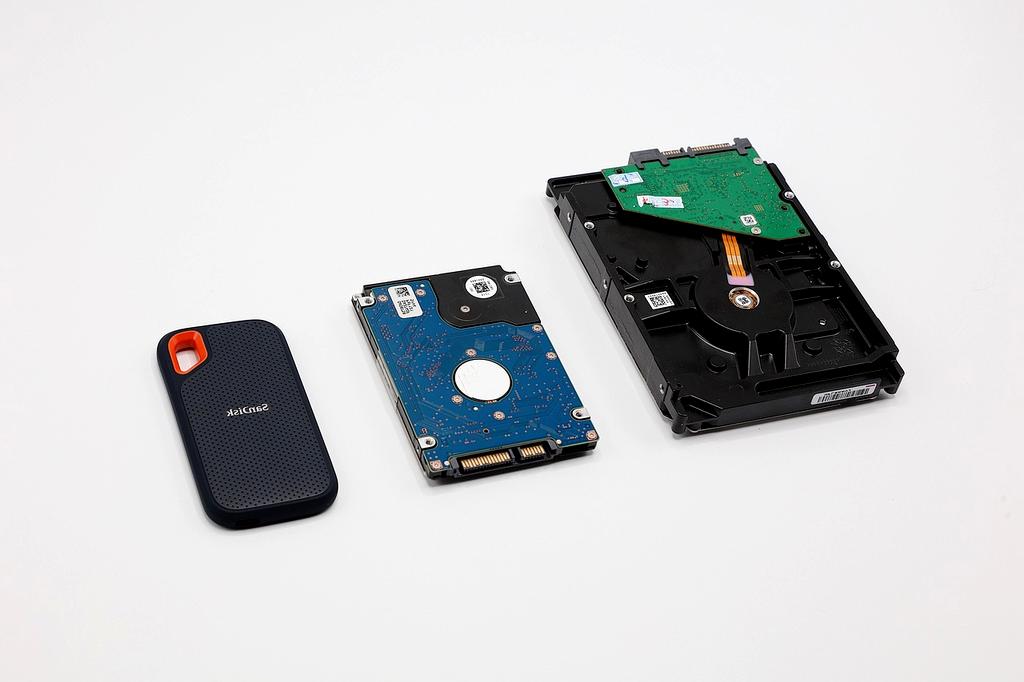
Data Storage Technologies
From Magnetic Disks to Lightning-Fast SSDs
Explore the evolution of data storage technologies that have revolutionized computing and changed how we preserve digital information forever.
Discover the Journey Compare Technologies